Gneuss enabling the use of Microfibrillated Cellulose in polymer melts for thermoplastics
Andrea Kossmann, Guest blogger | September 11, 2019
The pursue for a more efficient and increasingly EHS improved way of incorporating microfibrillated cellulose into polymers for polymer melts (thermoplastics) has been going on for years. Thermoplastics are an important source for many final products and applications. By introducing microfibrillated cellulose into polymers by the means of liquid suspension, Gneuss have been able to avoid the agglomeration of powder form similar particles, as well as improve the EHS profile of such a process.
The benefits of improving dispersion of the particles in the polymer melts
Gneuss, a German leading company on polymer processing and recycling, has come up with a very interesting way of avoiding these issues. Gneuss found that with their new state-of-the-art technology they allowed for significantly better dispersion of the microfibrillated cellulose compared with conventional processes. Thus, they could reduce the amount of additive needed, while at the same time obtaining the benefits.
An add-on benefit Gneuss found was that with their technology, the amount of additive needed was so low that there were negligible side unwanted side effects. The Gneuss process can, in addition to enable use of microfibrillated cellulose for polymer melts, allow for to use carbon nanotubes to achieve conductivity in the polymer without the need for the polymer to be completely black. Thus, according to Gneuss, "a colored, conductive polymer is possible".
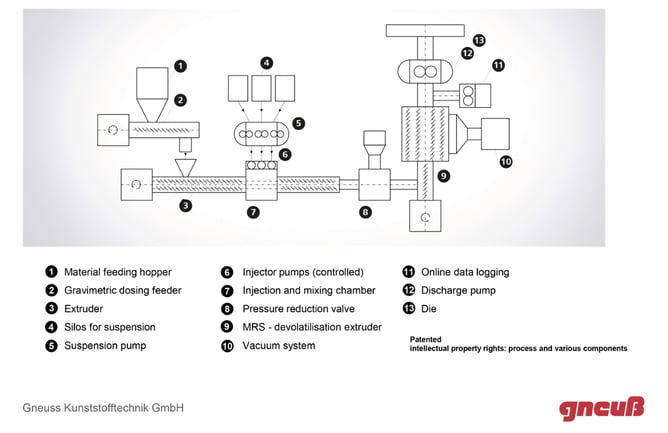
Figure 1: The Gneuss Nano Compounding Technology, courtesy of Gneuss Kunststofftechnik GmbH
The problems when incorporating typical nano particles in powder forms
The challenge when incorporating the nano particles into polymer melts is two-fold:
- The handling of extremely fine powders can require extensive safety measures
- The agglomeration of nanoparticles take place, and thus decreasing the positive alterations to the polymer

Figure 2: Agglomeration of nano particles in powder form (left) vs suspension of Exilva MFC (right)
With the new Gneuss Nano Compounding Technology, they allow for microfibrillated cellulose to be introduced into polymers. When they do this via a suspension, they at the same time increase the EHS benefit at the manufacturing site, due to less handling of hazardous fine powders. This will enable a smoother running process and an improved EHS profile for the users of this technology.
Interested in learning more about this Technology?
Contact Gneuss at:
Gneuss Kunststofftechnik GmbH
Andrea Kossmann
Mönichhusen 42
32549 Bad Oeynhausen
Tel: +49 5731 5307 10
www.gneuss.com